The Probability of Either One Event or Another
Sometimes there is more than one event together - combined probability. Here's an example:
This table is the probability of a book chosen at random falling into one of these three catagories.
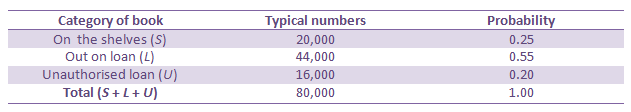
The probability that a random book is either out on loan or on an unauthorised loan is:
= 60000 ⁄ 80000
= 0.75
This could also be written as:
= n(L) ⁄ n(Ɛ) + n(U) ⁄ n(Ɛ)
P(L ∪ U) = P(L) + P(U)
∪ is the union symbol which means 'or'. There is another symbol we'll look at later, ∩ which means 'and'. You can tell these apart by thinking fish n' chips = fish and chips - so the other one has to be or.
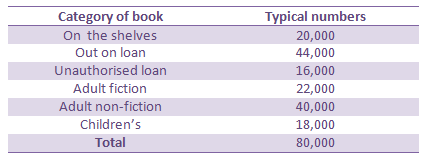
Find the probability that the next book chosen at random will be either out on loan or an adult non-fiction book.



